MS - EXCEL
Hello friends, in this post today, we learn about what is MS Excel and why we use MS Excel. so lets start...
GETTING STARTED WITH EXCEL
MS-Excel is spreadsheet programs that allow you to organize, analyses, and graph information on your computer desktop. A spreadsheet allows you to apply a variety of calculations and is a very convenient tool for preparing Budgets, Annual Reports, Production schedules, Income statements and scores of other thinks.
SPREADSHEET
A spreadsheet refers to the presentation of data in columns and row also called as a worksheet. Spreadsheet programs do for figures , statistic data chart ,and forms what word processor do for writing .A spreadsheet is like an automated ledger . There is no need to add and subtract column of number by hand ,or even with a calculator .They also have a powerful program for graphical preparation of numerical data.
LAUNCHING MS EXCEL
Excel can be open in one of the following ways:
1) Click Start menu-> All Programs->Microsoft Office-> Microsoft Office Excel 2007
OR
2) you can also type 'EXCEL' under open text box in run dialog box (Start button->Run) to launch the program.
MICROSOFT EXCEL
Microsoft Excel for is a powerful spreadsheet application that can be used for managing, analyzing and presenting data in a graphical manner.
 |
| Excel sheet full detail |
Excel has three components that perform three different tasks-
1. THE SPREADSHEET COMPONENT
It displays and analyses text and numbers in rows and columns.
2. THE DATABASE COMPONENT
It manipulates lists of information.
3.THE CHART COMPONENT
It produces charts which help to present data in a graphical manner.
WORKBOOK - Excel document are called workbook. A workbook is an Excel file where the users store his data. Each workbook consists of several worksheets. Hence, a workbook is said to be a set of worksheets grouped together. The individual sheets of a workbook are identified by labeled tabs called as sheet tabs.
WORKSHEET - A worksheet is a sheet made up of Rows and columns. It's used for planning a project or financial documents of an organization. Worksheet refers to the actual document you create by using the spreadsheet program. A worksheet always stored in a workbook.
CHARTSHEET - Chart sheet is a separate sheet in a workbook that contains only graphs or charts. It is useful when you want to see a chart or tabular data separated form other type of data.
ROW - A row is horizontal block of cells that runs through the entire width of the worksheet. A worksheet contains 1,048,576 rows. The first row is numbered 1, the second 2, and so on.
COLUMNS - A column is vertical block of cells that runs through the entire worksheet. A worksheet contains 16,384(A to XFD) columns. The First column is A and the last column if the worksheet is the XFD is the 16,384th column.
CELL - A cell is the intersection of row and column. For ex:-G9.
FORMULA - Formula is equations that perform calculations on the values in worksheet. A Formula always begin with equal (=) sign.
FUNCTION - Functions are predefined formulas that take value or values, perform complex calculations by using a specific value in a particular order to give a result. Functions are used to simplify the formulas that perform lengthy r complex calculation.
What is M.S. Excel
MS Excel is a part of Microsoft Office known as a Spread Sheet package in which data is written in rows and columns and then any type of calculation on it. can do. Such as mathematical statistical and financial etc. In this, you can analyze the data and make its report. In this, data can be displayed as a graph.
Definition of MS Excel: Microsoft Excel is a software created by a Microsoft company that allows the user to organize, format and calculate data using an Excel formula in a spreadsheet system. This software is a part of Microsoft Office, which has other applications besides Excel.
As we have already known that MS Excel is a spreadsheet application which is used to accomplish a lot of tasks like data calculation, formatting etc. The full name of MS Excel is Microsoft Excel. Here we will know about its layout, what are the options in it.
To work in this application and to run it properly, you need to understand its layout. You should know what are the names of the options that show its interface and what can we do with them. Next, we will learn about the options present in the interface. Here you are shown the layout of Microsoft Excel 2007 version with screenshot
Title bar: The bar that you will see in the top part of MS Excel, ie the center at the top, is the Title Bar. Here, the name of any file you are working in will appear. If you are working in a new document, then its name will be Book1, when you go to save it, then you can save it by keeping the name of your choice. Now your name will appear in place of Book1. In its right side corner you have 3 buttons. These three buttons have different functions which I am telling you further.
Minimize - When we click this button, Microsoft Excel or any program that is open, it goes down in the taskbar. You can open it again at any time by clicking in the taskbar. We use it only when we need to open some other application in the middle while working.
Using the Maximize - Maximize button, we can change the box of Microsoft Excel or any other program according to your mind. They can work by adjusting the width and length of the program's window. By clicking this button again, we can bring the application back to full screen.
Close Button - This button is in red color, when we click on it, the application or program closes.
Office Button: In Microsoft Excel, the Office Button is a core part. This button is in the left side corner. There are many types of options in this, such as New, Open, Save, Save as, Print, Prepare, Send etc.
Quick Access Toolbar: Quick Access Toolbar located in the title bar is also a major option. We use this toolbar to bring more commonly used commands there. This means that for every option or command that you use repeatedly, you have a delay in going to the menu and clicking on it, then you can add its command here, then you do not have to go in too much. is. That command gets added to the quick access toolbar and you can use that command directly from here.
Menu bar: Menu bar is located just below the title bar. In this, the option used in MS Excel is a special task for everyone. And inside each tab it has its own ribbon which has many tools.
Ribbon: Ribbon occurs below the menu b. There is a different ribbon for each tab of the menu bar. Inside every ribbon, there are many options in which everyone has different work and every tool is very important. Here you can see the area of ribbon as a red colored box.
Name Box: The small box you see on the left side under Ribbon is the Name box. In this box, you see the name of each cell. When you enter the name of a cell in it, you can find it.
Formula Bar: The box to the right of the Name box is the Formulabar, in which we can do our work by writing a formula, apart from this, the cell in which we work or write anything is visible in the formula bar.
Text Area or Main Working Area: Here the cells appear as rows and columns. We do all our work on this. That's why we make a table, put data in it, do calculations. We also call this sheet.
Status Bar: It is just below the text area. Here there are options to set sheet tab, page layout selector, and zoom level.
Sheet tab: It is located in the status bar, that too on the left side. Here we can add different sheets within the same file, for that we just get the option to create a new sheet tab copy or new sheet, so that you can easily create multiple sheets inside a file.
Page Layout Selector: On the right hand side of the sheet tab is the page layout selector. Using it, we can see the sheet in different layout. There are Normal, Page layout, Page Break Preview, from which you can see your page and make the setting of the page.
Zoom Level: Page Layout Selector is the option of zoom level on the right side. Through this we can see the sheet by adjusting it in small size. When the sheet becomes very large, then this option is of great use to us.
How to start ms excel
Clicking on Start-> All Programs-> MS Office-> MS Excel starts a new Excel file.
Work Book: - (Work Book) This is a document of Excel, it has 255 work sheets in it, in general it shows three sheets in it.
Spread sheet: - These are the pages of an Excel document, where does this work sheet also go? It has 65,536 RAW and 256 columns inside it. Where the RAW and the columns intersect, a rectangular area is called, which is called the cell. Cell is the smallest and important unit of Excel document. In which data or information (information) is kept safe and any type of calculation can be done on it. Every cell has its own unique address or reference number. Which is obtained by writing columns and RAW in sequence.
Cell Reference: - Every cell has its own unique address or reference number. Through which the data of the cell is obtained. It is of 4 types.
(1) Relative Reference
(2) Absolute Reference
(3) Relative and Absolute Reference
(4) Absolute and Relative Reference
1. Relative Reference: - This reference is obtained by writing columns and RAW in sequence. In this, the reference of one cell is changed to the reference of the other cell according to the first cell. Using it makes calculations easier and quicker. This cell reference is written as follows. Such as - a2, b2 and c3 etc.
2. Absolute Reference: - In this the reference is taken with doller mark ($). In this, the reference of one cell does not change to the reference of another cell. Such as- $ a $ 2, $ b $ 2 and $ c $ 2 etc.
3. Relative and Absolute Reference (Relative and Absolute): - In this, the column is relative and Raw is absolute. In which the column changes to a reference to another cell. But RAW does not change. Such as- a $ 2 and c $ 3. etc.
4. Ablolute and Relative Reference (Absolute and Relative Reference): - In this, the column is written as absolute and Raw is written as Relative. In which the column gets fixed. And RAW varies. Such as- $ A2, $ B2, and $ C2 etc.
THE SCREEN ELEMENTS OF MS EXCEL WINDOW
When Excel is loaded, two windows appear which nested one within the other is.
 |
| Ms. Excel Window Home Page |
1. TITLE BAR - It appears at the top of the MS-Excel window .Application's control box located at the left end of the title bar. At the right end of the Title bar are three boxes .These boxes are the minimize, maximize or restore and close button.
2. RIBBON - Click on different tabs to get the respective ribbon.
> Home: You will probably spend most of your time with the Home tab selected. This tab contains the basic Clipboard commands, formatting commands, alignment command, style commands, and commands to insert and delete rows or columns, plus an assortment of worksheet editing commands.
 |
| Home |
> Insert: Select this tab when you need to insert something in a worksheet-a table, a diagram, a chart, a symbol, and so on.
 |
| Insert |
> Page Layout: This tab contains commands that affect the overall appearance of your worksheet, including setting that deal with printing.
 |
| Page Layout |
> Formulas: Use this tab to insert a formula name a range, access the formula auditing tools, or control how Excel performs calculation.
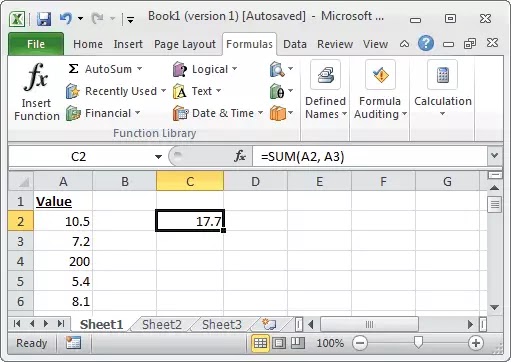 |
| Formulas |
> Data: Excel's data-related commands are on this tab.
 |
| Data |
> Review: This tab contain tools to check spelling, translate words, add comments, or protect sheets.
 |
| Review |
> View: The View tab contains commands that control various aspects of how a sheet is viewed. Some commands on this tab are also available in thestatus bar.
 |
| View |
3. FORMULA BAR - It is below the formatting Tool and is made up of three parts; the reference area at the left end shows the address of the active cell. The middle and right area are used to display or edit data present in the cell.
 |
| Formula bar |
4. SHEET TAB - The Sheet Tab located at the bottom of worksheet and holds a number of worksheet. Sheet tabs and the navigation buttons belong to the extreme left end of the horizontal scroll bar. With the help of sheet tab you can move to another worksheet or use the navigation buttons to scroll through the sheet tab.
5. STATUS BAR -The status bar, which is a horizontal area at the bottom of the document window, provides information about the current state of what you are viewing in the window and any other contextual information.
CREATING A NEW WORKBOOK
- Click on Ms-Office Button.
- Choose New option from menu. New Dialog box appears.
- In New dialog box, Click Blank Workbook and then click on Create button.
WORKING WITH WINDOW
>>New Window - A new window of the selected document is displayed .This lets you look at different areas of the same worksheet at the same time.
>>Arrange - The user may want to see several worksheets at the same time so that he is able to view information that is stored in more than one sheet. To arrange windows the Windows, Arrange command is used. The Arrange window dialog box appears as shown below.
 |
| Arrange Window |
>>Hide - Suppresses the display of the selected worksheet; removes the hidden workbook name from the filename list at the bottom of the Window menu.
>>Unhide - Prompts you for the name of the hidden workbook .Once entered, the workbook is unhidden.
>>Split - Split the displayed worksheet into four "Panes" .If the cell pointer is in A1, The split divides the worksheet into four equal panes .Otherwise, the split occurs at the upper left -hand corner of the selected cell. The panes are synchronized so that moving the cell pointer moves all adjacent cells in unison.
>>Freeze Panes - Use to freeze column and row title in place while interior values are scrolled horizontally and vertically.
WORKING WITH MULTIPLE WORKBOOKS
When you're working on a project in which you need to use several different workbooks at the same time, you can save a list of those workbooks, along with their arrangements on the screen, their print areas, and soon.Thatway. whenever you have to stop and then resume your work, all you have to do is open the list (Excel calls it your workspaces), and presto! All the workbooks in the workspace are open and in their reassigned locations.
CREATE A WORKSPACE
- Open all workbooks you need for the project, and arrange them on the screen exactly as you want them.
- Choose Save Workspace from the View Tab to display the Save Workspace.
- Select a location for the workspace.
- Type a name for the workspace.
- Click Save and then work on your workbooks as usual. If you modify the arrangement or change other settingyou'llwanttouseinthe future, save the workspace again before you close the workbooks.
- To return to the workbooks after you've closed them, choose Open option, and locate and open the workspace.
WORKING WITH WORKSHEET
The worksheet is displayed as a grid of rows and columns. There are16,384 columns lettered A through XFD , and 1,048,576 numbered 1 through 1,048,576 . The address of the first cell in a worksheet is A1 and that of the last cell is XFD1 ,, 048,576.
=> ADDING A NEW WORKSHEET
i) Choose and click Insert option from the popup menu.
ii) Right Click on the worksheet.
=> REMOVING A WORKSHEET
i) Choose and click Delete option from the popup menu.
ii) Right-click on the sheet tab.
=> RENAMING A WORKSHEET
i) Select Rename option from the context sensitive popup menu, type the name and press enter.
ii) Double-click on the sheet tab of the worksheet you want to rename or right. Click on the tab, type the name and press enter.
iii) The current name will be highlighted. Type a new name and press Enter key.
=> MOVING OR COPYING WORKSHEET
i) Select Move or Copy Worksheet option from the context Sensitive popup menu, select the worksheet and press enter.
ii) Right click on the sheet tab.
RANGE
A range is a rectangular group of cells. The smallest range is a single cell, while largest encompasses all the cells in the workbook. A range can be contain cells from a single sheet only or can include cells from adjacent. Ranges are defined by the addresses of two opposite or diagonally paired corner cells separated by a colon (:) or two dots ( .. ). e.g. B4:H12 or B4 ... H12.
ENTERING INFORMATION
1. TEXT:-To enter text, the cell where data is to be entered is selected first and then the text is typed. The typed text appears in the active cell as well as the formula bar. Notice that the entry is always left -aligned in its cell.
2. NUMBERS:-Numbers are typed directly. Numbers can be entered with commas, dollar signs, percent signs, and scientific notation. Numbers can include numeric characters from 0 to 9 and any of the following special characters- +, -, (), /, $, %. etc. Notice that the entry is always right -aligned in its cell.
3. FRACTIONS:-To enter a fraction-
I. The whole number and the fraction should be separated by a space. For e.g. 2 3/4.
II. If the fraction does not have the whole part -
A zero should be placed in front of the fraction. For e.g. 0 2/3.
4. DATE AND TIME:- For a date or time to be displayed correctly, you must enter it
"In format", meaning that you must enter it in a format that EXCEL recognizes as a date or time. The following formats are recognized-
2/8/98 9:35 PM
9-Mar-97 9:35:45 PM
9-Mar 9:35
Mar-7
Two additional formats combine both date and time and take these forms-
3/8/98 9:35 3-9-98 9:35
FILL SERIES
Excel 2007 makes it very easy to enter a series of dates, numbers or text.
For ex: - you can insert column heading like Jan, Feb, Mar etc or enter number at equal intervals such as 2, 4, 6 etc. very easily.
You can enter the above type of series in two ways
- Using the mouse to drag the fill handle.
- Using a command that gives you the capability to create many types of series.
HOME TAB -> EDITING GROUP -> FILL
 |
| FILL SERIES |
BUILDING FORMULA AND FUNCTIONS
Formula in Excel: - One of the important features of a spreadsheet program is the ability to manipulation text and performs simple as well as complex calculations very efficiently. Excel help you quickly build formulas using your key board and mouse .Excel also provides Toolbar ,menu choices and functions you can employ to create and use complex formulas Formula can be of 3 types -
1. Text Formula -
It uses text and hence it is called a text formula. It may contain a text operator ampersand (&). For e.g.& A1.
2. Numeric formula -
They contain arithmetic operators like + ,-,*, /, ^ or %.For e.g. = A1+B1
3. Logical Formula -
They contain comparison operators like <,>, <=> =, <>. For e.g. = A1>34
Following rules need be remembered in case of formula;-
- A formula must always begin with an Equal to (=) sign. It can also begin with a "+' or "-? sign
- A formula can be up to 255 characters long ..
- It cannot contain spaces, except between a set of letters, numbers, or symbols enclosed in quotation marks.
OPERATORS TYPES
Operators are used to specify an operation, to be performed on elements of a formula. There are 3 types of operators
1. ARITHMETIC OPERATORS
Perform basic mathematical operations, combine numeric values and produce numeric results. The mathematical operators are:-
| Operator | Meaning |
| + | Addition |
| - | Subtraction |
| / | Divison |
| * | Multiplication |
| % | Percent |
| ^ | Exponentiation |
2. COMPARISON OPERATORS
They compaer 2 values to produce the logical value TRUE or FALSE.
| Operator | Meaning |
| = | Equal |
| > | Greater than |
| < | Less than |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| <> | Not Equal to |
3. TEXT OPERATOR (&)
Joins 2 or more text values to produce a single combined text value.
About Formulas
- Entering Formula:- We place the formula in the cell where we want to see the results. We type formulas in formula bar. Excel formulas always start with =(equal sign).
- Copying formula:- Similar to cell contents, formulae can also be copied from one location of the worksheet to another. Note that when a cell containing a formula is copied, only the formula is copied and not the cell contents.
- Moving formula: - Formulae can also be moved from one worksheet location to another. When formulae are moved, they automatically change relative to the location to which they are moved. This is known as "Relative Addressing".
- Displaying Formula: - A cell containing a formula normally displays the formula's resulting value on the worksheet when the user select a cell containing formula, the formula is always display in the formula bar. If you want to display the formula in the cell simply double click on that cell containing a formula.
ADDRESSING METHODS
(A) RELATIVE ADDRESSING - In relative addressing method address changes relative to the location where the formula is either copied moved.
For e.g. formula was copied from column A to B, the formula =A1+A2 has become =B1+B2.
This ability to adjust a formula from one location to another is called as Relative addressing.
(B)ABSOLUTEADDRESSING- In this method entire address is locked or fixed to a particular cell no matter where the formula is copied or moved. An absolute address always points to exactly one address. In absolute address '$' sign is used to indicate the absolute position of the cell addresses. For e.g. $D$5 means the row and column address is fixed.
(C) MIXED ADDRESSING - Mixed address is combination of Relative and Absolute Address. The Possible combinations are -
I. $A3 - In this case column 'A' is fixed, row 3 varies.
II. C$3 - In this case column C varies and row 3 is fixed if the formula containing this address is Copied or moved.
FUNCTIONS
Worksheet functions can often be used by themselves as stand - alone formulas, or they can be built into complex formulas of your own creation .For instance, the SQRT () function finds the square root of a positive number. Functions are special pre-written formulas that take a value or values, perform an operation, and return a value in the cell in which they are entered.
PART OF THE FUNCTION: - Function consists of function name and (usually) arguments .For instance, SQRT is the function, while the value being evaluated is the argument.
The syntax for entering functions is as follows, = Function name (value ... )
THE FUNCTION WIZARD - Excel's Function Wizard greatly simplifies the use of functions. It leads you through the necessary steps, show the result as you work.
- Start by activating the cell where you want to paste the function.
- Begin the formula with an equal sign (=), and place the insertion point where you want to insert the function.
- Click the Function button on the Standard toolbar, or choose Insert Function from Excel's Insert menu. The Function wizard's Step 1 window appears . The function wizard lists function within the eleven categories.
- Pick a category from the list on the left, then scroll in the list on the right to find the desire function.
- Click to pick the function Its name is display in the Name Box on the formula bar.
- Click the Next button and you will see Wizard dialog box .Here you see a list of argument that are require and possibly some that are option.
- You can type directly in the Wizard's entry boxes or use your mouse to point to cells containing the data you wish to use as arguments.
- As you work, the Wizard will show the result of its calculations in the value area at the top right corner of the dialog box.
- Click the finish button when your formula is complete.
FUNCTION CATEGORIES
Excel functions can be categorized as follows:-
MATHEMATICAL FUNCTIONS
| FUNCTION | RETURNS |
| =Abs(Number) | Returns the absolute vale of number. |
| =Ceiling(Number, Sign) | Rounds a number up, to the nearest integer. |
| =Floor(Number, Sign) | Rounds a number down, to the nearest integer. |
| =Even(Number) | Return a positive Number. |
| =Fact(Number) | Returns a factorial of a number. |
| =lnt(Number) | Round a number down to the nearest integer. |
| =LCM(NI ,N2) | Returns the least common multiple. |
| =Log(Number, Base) | Returns a logarithm of a number to the base you specify. |
| =Mod(Number, Divisor) | Returns the reminder after a number is divided by a divisor. |
| =Odd Number | Rounds a positive number to the down nearest odd integer. |
| =Pi() | Returns the value of Pi. |
| =Power Number, Power | Returns the resuft of a number raised to a power. |
| =Product NI ,N2,N3) | Mufti lies all the numbers given as arguments. |
| =Quotient(Numerator, Denominator) | Returns the integer portion of a division. |
| =Round Number,Num Di its) | Rounds a number to a s ecified number of digits. |
| =Trunc(Number,Num_Digits) | Truncates a number to an integer by removing the decimal. |
| FUNCTION | RETURNS |
| =Average (nl , n2...) | Average of arguments |
| =Count (nl , n2...) | Counts how many arguments are present in the list of the arguments |
| =Max (nl, n2...) | Maximumyalue in a data set |
| =Min(n1 ,n2, ...) | Minimum value in a data set |
| =Countif(Range, Criteria) | Counts the number of cell within a range. |
| =Averageif(Range,Criteria, Average_range) | Find the average for the cells specified by a given condition or criteria. |
DATE AND TRIME FUNCTIONS
| Function | Returns |
| =DATE(Y,M,D) | Returns the number that represent the date. |
| =Today() | Returns the current date. |
| =Now() | Returns the current date and time. |
LOGICAL FUNCTIONS
| Function | Returns |
| =And (Logicl ,Logic2) | True if any argument is true |
| =False | Logical value false |
| =Not ( ) | Returns true if its argument is false |
| =lf(test, true, false) | Returns a specified value depending on the outcome of the test |
| =Or (Logicl ,Logic2) | True if any argument is true |
| =True( ) | Logical value true |
FINANCIAL FUNCTION
| Function | Returns |
| =SLN(cost,salvage,life) | Returns the straight line depreciation of an assets for one period. |
| =PMT(rate,nper,pv,fv,type) | Calculates the payments for a loan based on constant payment and constant interest rate. |
| FUNCTION | RETURNS |
=Char(Number) |
Returns the character specified by the Code Number from the character set for your computer. |
| =Code(Text) | Returns a numeric code for the text. |
| =Concatenate(Text1, Text2) |
Join Two or More string in a one test string. |
| =Exact(Text1,Text2) | Compares two string s and returns True if they are exactly the same otherwise False. |
| =Find(Find_Text, Within_Text, Start_Number) | Return the starting position of one text string with another text string. Find is Case-Sensitive. |
| =Left(Text, Num_char) | Returns the specified number of string from left. |
| =Right(Text, Num_char) | Returns the specified number of string from right. |
| =Len(Text) | Returns the number of character in a text string. |
| =Lower(Text) | Converts all latter in a text string of lowercase. |
| =Upper(text) | Converts all latter in a text string of uppercase. |
| =Mid(text, Start_num, Num_char) | Returns the character from the middle of text string. |
| =Proper(Text) | Capitalize the first latter in a text string. |
| =Replace(Old_text, Start_num, Num_char, New_Text) | Replace a part of text string with a different text string. |
| =Rept(Text, Num_Times) | Repeat a text a given number of times. |
| =Search(Find_text, Within_text, Start_Number) | Return the starting position of one text string with another text string. search is not Case-Sensitive. |
| =Substitute(Text, Old_text, New_text, lnst_num) | Replace exsting text with a new text in a text string. |
| =Trim(text) | Remove extra spaces from a text string. |
 |
| Change Chart Type |
- Select the cells where you want to include pivot table Click on the Insert Tab and in the table group.
- Choose Pivot Table. Pivot Table dialog box appears.
- Click OK.
- After that an empty Pivot Table report is added to location that you entered with the pivot field list.
- Add the pivot table field list.
 |
| Create Pivot Table |
- Select the cells that you want to format.
- Under Home tab, click arrow next to Style group.
- Sedlect and click the cell style that you want to apply.
- Home Tab, Click arrow to next Style group and then select New Cell Style.
- Style dialog box appears.
- In the style dialog box,ttype the name for the new cell style in the Style name.
- Click on Format button and add desired format.
- Click OK.
- Select the cell or range.
- Choose Data tab -> Data Tools group -> Data Validation. Excel displays its Data Validation dialog box.
- Click the Setting tab.
- Choose an option from the drop-down box labeled Allow. The contents on the Data Validation dialog will change, displaying controls based on your choice. To specify a formula, select Custom.
- Specify the conditionsby using the displayed controls.
- (optional) Click the Input Message tab and specify which message to display when a user selects the cell.
- (optional) Click the Error Alert tab and specify which error message to display when a user makes an invalid entry.
- Click OK.
- Choose Data -> Data Tools -> Consolidate. Excel displays its Consolidate dialog box.
- Use the Function drop-down list to select the type of consolidation summary that you want to use. Use Sum for this example.
- Enter the reference for the first worksheets to consolidate and click on Add to add to the reference list.
- Because the worksheets aren't laid out the same, select the left column and Top row check boxes to force
- Excel to match the data by using the labels.
- Select the Create Links to Source Data check box to make Excel create an outline with external reference.
- Click OK to begin the consolidation.

CONSOLIDATE
- Smallest to Largest
- Largest to Smallest
- A to Z
- Z to A
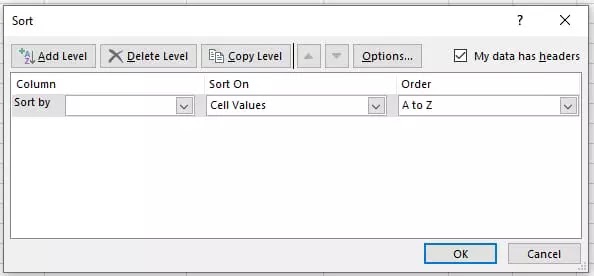 |
| Sort |
- Select the column or portion of columns whose contents you want to sort.
- Choose Sort from the Data Ribbon to display the Sort & Filter Group.
- Specify whether or not the columns have the header name.
- Specify which column you want to sort by.
- If you want to refine the sort by also sorting by a second column, specify the column and then the sort order.
- Choose the column and sort order if you want the sort to be further refined by a third-level sort.
- Click you want to change the type of sort, conduct a case-sensitive sort for text, or sort by rows instead of by columns.
- Click OK to sort the data.
- Select a cell in the list you want to filter.
- On the Data ribbon, point to Sort & Filter, and then click Filter.
- Click the arrow in the column that contains the data you want to filter.
- To filter the list by one value in the column, select the value:
- To filter the list by two or more values in the column, or to apply comparison operators other than and, click Custom.
- In a blank row, type or copy the criteria labels you want to use to filter the list. These labels should be identical to the labels of the
- Columns you want to filter.
- In the rows below the criteria labels, type the criteria you want to match. Leave at least one blank row between your criteria Values and your list.
- Click a cell in the list.
- On the and then click Advanced Filter. The Advanced Filter dialog box is given below.
- To filter the list by hiding rows that don't match your criteria, click Filter the List, In-Place. To filter the list by copying rows that match your criteria to another area of the worksheet, click Copy to another Location, click the
- Copy To box, and then click the upper-left corner of the paste area.
- In the Criteria Range box, specify the criteria range, including the criteria labels.
 |
| SUBTOTAL |
 |
| GOAL SEEK |
| TS CP L Group Industries. |
| New Campus-III Sectr-D, G reater Noida |
| Emp Code | Emp Name | Joining DATE | Post | Basic Salary |
| M0121 | Prena Sharma | 4/1/2005 | Manager | 18000 |
| M0122 | Rohit Bajaj | 9/2/2008 | Clerk | 15000 |
| M0123 | Chetan Bhagat | 5/4/2007 | Mkt | 13800 |
| M0124 | Vishal Tiwari | 2/5/2009 | Fin | 11650 |
| M0125 | Kabeer Khan | 6/9/2008 | Sales | 12840 |
| M0126 | Javed Ali | 1/2/2009 | Fin | 10000 |
| M0127 | Sandhya Sharma |
6/6/2007 | Mkt | 9800 |
| M0128 | Naina Kapoor | 4/2/2009 | Clerk | 13600 |
| M0129 | Sidhartha Malhotra | 2/1/2010 | Fin | 14300 |
| M0130 | Karan Roy | 5/9/2012 | Mkt | 10960 |
- Format the top two values of Net Salary.
- Basic salary value between 13,000 to 18,000.
- Split the workbook and remove split.
- Freeze the Row& Unfreeze it.
- Hide & Unhide Gridlines.
- Change Zoom Size of window.






.jpg)






0 Comments